In addition, small businesses that need to remain nimble and creative often find the Six Sigma system of process analysis stifling, bureaucratic and overly time consuming. Six Sigma is a proactive methodology that identifies and provides recommendations for potential problems before the company incurs any form of loss. Six Sigma may be implemented in several categories within a business, directly impacting profitability and reducing costs. It is significant to note that for B2B customers, the Six Sigma standard for manufacturing products is a credible endorsement.

Leverage project data
Outside of a manufacturing operation, Six Sigma often fails to yield the kind of results needed to justify such a time-consuming and expensive management change. The term “sigma” is a measurement of how far from perfect a system or producer can get—by Six Sigma standards, companies should reduce manufacturing defects to less than 3.4 per 1 million units. This chapter is devoted to the discussion of the which tax form should i use. In various sections, we have detailed the advantages and disadvantages, limitations, and pros and cons of Six Sigma philosophy. Enough care is taken to explain the concepts from a practitioners’ and customers’ point of view.
Focused Only on the Quality
- They benefit from a rigorous methodology that encourages systematic problem analysis and the implementation of sustainable solutions.
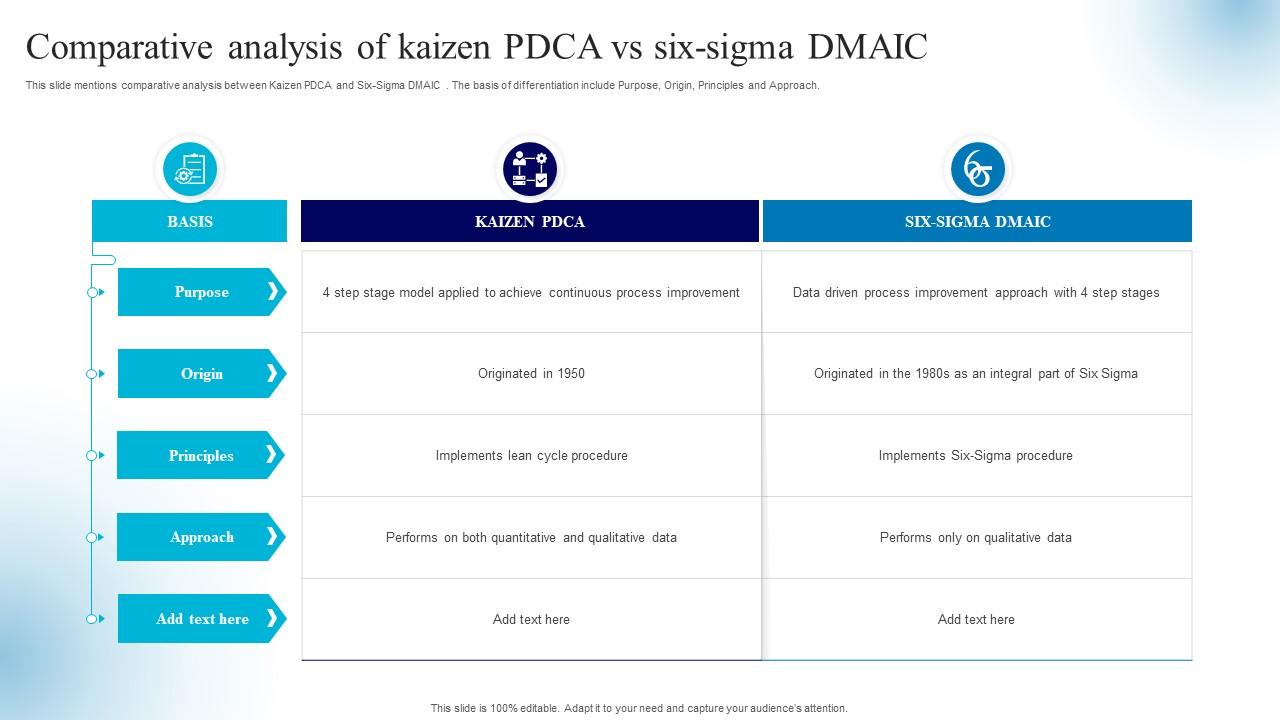
- This article will go into a more detailed definition of Six Sigma, and then look at some of its tools, certifications, methods, stages & steps, and guiding principles.
- In addition, small businesses that need to remain nimble and creative often find the Six Sigma system of process analysis stifling, bureaucratic and overly time consuming.
- Motorola Company, further improved the six sigma methodology and gradually elevated optimization in its processes.
That is because the cost savings made by virtue of eliminating returned products, costly reworks and defective products, are only a process improvement byproduct. With time, progressive quality improvement may lead to increased overhead and capital costs, thus canceling out initial savings made. Since Motorola’s introduction in 1986, it has also been widely used as a quality measure that seeks near elimination of defects by employing statistical methods. The measurements adopted are founded on process strategies highlighting variation reduction, which theoretically, triggered improvements in the actual process. That is because the cost savings made by virtue of eliminating returned products, costly reworks, and defective products, are only a process improvement byproduct. With time, progressive quality improvement may lead to increased overhead and capital costs due, thus canceling out initial savings made.
Six Sigma Certification and Belt Rankings
A small business that achieves the coveted Six Sigma quality certification will certainly stand out among its competitors. Because Six Sigma is applied to all aspects of the production and planning process, it may create rigidity and bureaucracy that can create delays and stifle creativity. For example, an inexpensive measure that carries a risk of a slightly higher defect rate may be rejected in favor of a more expensive measure that helps to achieve Six Sigma, but adversely affects profitability. Sometimes when a company implements Six Sigma, problems arise as the company focuses on Six Sigma endorsed policies only and forgets about its specific mission statement or policies. For small businesses, it may constrain new ideas favoring creativity and innovation, which require some risk-taking to implement. Companies have to find certified Six Sigma institutes to train their employees or conduct in-house training without formal certification.
Top 10 Cons & Disadvantages: Six Sigma Certification
This could also be the stage where you begin to design highly data-driven experiments. When implementing Six Sigma, it’s a good idea to know beforehand which of the following practices you should use. It shows the relationship between two different data sets operating in the same existing process. In Six Sigma, this shows what happens to one process and its set of data when changes are made to another. When something goes wrong, that is the effect of a cause, and therefore cause and effect analysis is central to Six Sigma problem solving. To analyze cause and effect, you need to identify the problem, make clear the factors and context, identify possible causes, and propose solutions.
In short, Six Sigma can generate significant performance gains for an organization, but this methodology is limited in scope. Its implementation should therefore be restricted to the optimization of specific types of processes, and different frameworks should be applied to enhance other areas of the business. Six Sigma is a rigorous and complex methodology that requires a deep understanding of statistical analysis and problem-solving techniques. This complexity can make adopting and implementing it is challenging for organisations without proper training and support. It establishes a culture of ongoing organisational improvement, where processes are regularly reviewed, analysed, and optimised. This commitment to continuous improvement leads to sustainable long-term results and ensures that the organisation stays ahead of its competitors.
Getting rid of inefficiencies like bottlenecks, wasted resources, or defective results is what Six Sigma is all about, and you need to keep such an inefficiency-seeking focus always in high gear. This is particularly key when talking about processes that can be done quicker, cheaper or more consistently. At the verify stage of DMADV Six Sigma, it’s a good idea to get all the stakeholders together. Everyone from the team working to the customer, to see if all agree that the selected design matches the expectations set out in the define stage. If all is well, this stage must have a plan to keep the new process implemented in a sustainable way.
Over the years, Six Sigma has been hailed as a solution to operational inefficiencies, leading many organizations to adopt its principles. With its data-driven methodology, Six Sigma focuses on eliminating defects and ensuring process improvements. Six Sigma emphasises process optimisation by identifying and eliminating waste and inefficiencies. By streamlining processes and reducing variation, organisations can achieve higher levels of productivity and efficiency.
Obtained through training and passing a set examination, this certification is offered in various belts, including Yellow, Green, Black, and Master Black. Each belt signifies a different level of expertise and knowledge in Six Sigma methodologies. Businesses use the Six Sigma methodology to improve processes by identifying the errors that lead to defects and implementing new management systems once errors have been addressed.
Because, if a process deviates too much from what it is expected to produce, the solutions become more difficult and complex. All this leads to a gradual improvement in the processes of a business and ultimately the business becomes more competitive. The main principles of Six Sigma are customer focus, data-driven decision-making, and a systematic approach to process improvement. By incorporating these principles, organizations can strive for operational excellence and enhanced customer satisfaction.
